Perched at a staggering 8,844.43 meters above sea level, Mt. Everest commands awe from climbers and sightseers alike. Straddling the border between Tibet (China) and Nepal, Everest reigns as the planet’s loftiest peak and draws thousands each year eager to glimpse its legendary heights. In this guide, we’ll navigate every facet of the Mt. Everest map, from the Tibetan north side to Nepal’s southern approaches, trek itineraries, climbing route diagrams, costs, risks and practical tips.
1. Mt. Everest on the Map: Geography and Access
Everest lies at the eastern end of the Himalayan range, rising where the Tibetan Plateau meets Nepal’s rugged Khumbu region. The mountain’s two flanks share equal claim to its peak, but access differs markedly:
- Tibetan North Side
Approached via Shigatse Prefecture in Tibet, China, the north side features the Tingri plateau and the North Base Camp at 5,200 m. A network of paved roads and off‑road tracks brings travelers within reach by vehicle, requiring moderate trekking or shuttle bus transfers. - Nepalese South Side
Accessed through Kathmandu and the Sagarmatha National Park, the south side entails a classic trekking route from Lukla (2,860 m) to South Base Camp (5,364 m). Nepal’s side is celebrated for Sherpa culture, teahouse lodges and dramatic icefalls.
A comprehensive Everest map will illustrate both approaches, with contour lines for altitudes, marked trails, settlement locations, strategic passes and permits required at border checkpoints.
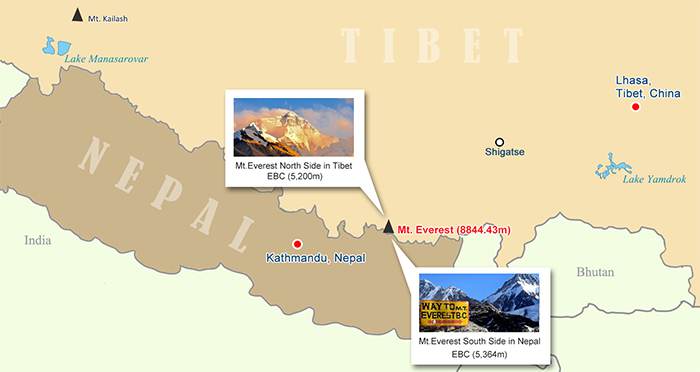
Mt. Everest on the Map
2. North Base Camp (Tibet)
Location: Tingri County, Shigatse Prefecture, Tibet (5200 m)
Transportation:
- By Tour Bus: Paved roads lead from Lhasa or Shigatse to the town of Old Tingri. From there, shuttle buses navigate a rough track directly to the base camp gate.
- By Trekking: A 2–3 day hike from Old Tingri follows high desert landscapes and yak pastures, offering acclimatization benefits.
Documents:
- Tibet Travel Permit (also called China Tibet Visa)
- Alien’s Travel Permit for border zones
Best Touring Seasons:
- Spring: April to mid‑June (warm days, clear skies)
- Autumn: September to November (stable weather, fewer clouds)
Scenic Highlights:
- Breathtaking panorama of Everest’s north ridge and summit icecap
- Sweeping vistas of neighboring peaks like Cho Oyu, Shishapangma and Lhotse
Accommodation:
- Local‑run expedition tents with basic heating
- Group‑style camps offering simple meals and communal dining
On an Everest map, mark North Base Camp with elevation points, road routes from Lhasa (3,650 m) via Gyantse and Shigatse, and trekking tracks that snake across the plateau.
3. South Base Camp (Nepal)
Location: Sagarmatha National Park, Nepal (5,364 m)
Transportation:
- Trekking Only: No road reaches the southern camp. The standard route begins with a flight to Lukla, then a 10‑day multi‑stage trek through Namche Bazaar, Tengboche and Dingboche.
Documents:
- Passport
- Sagarmatha National Park Entry Permit
- Khumbu Pasang Lhamu Rural Municipality Permit
Optimal Viewing Time:
- October to November, when monsoon clouds clear and days remain crisp
Scenic Highlights:
- While the Everest summit itself is partially obscured by neighboring Nuptse and Lhotse, the approach offers iconic views of the icefall, glacier tongues and Everest’s south face.
- Gokyo Valley side trek (optional) showcases turquoise lakes framed by snow‑capped peaks.
Lodging:
- Tea houses and trekking lodges with shared rooms and chow hall meals
- Tent camping for those on guided climbing expeditions
On a Nepal Everest map, trace the Lukla–Everest Base Camp trail, noting surgical switchbacks, villages, teahouses and high camps. Highlight side routes to Gokyo Lakes and Cho La Pass for adventurous trekkers.
4. Lhasa to Everest Base Camp: The Classic Tibet Tour
One of the most revered overland journeys in Tibet runs from the capital, Lhasa, to the North Base Camp:
Lhasa (3,650 m):
- Potala Palace, Jokhang Temple – Acclimatization and cultural immersion.
Gyantse (3,950 m):
- Palcho Monastery, Kumbum Stupa – Tibetan artistry in a fortress setting.
Shigatse (3,840 m):
- Tashilhunpo Monastery – Seat of the Panchen Lama.
Old Tingri (4,350 m):
- High plateau landscapes and nomadic yak herds.
North Base Camp (5,200 m):
- Everest viewpoint and glacier observations.
This scenic itinerary eases altitude gain (approximately 1,550 m over 7–8 days) and is fully drivable with occasional short treks. A detailed Lhasa–EBC map will mark each overnight stop, road gradients and scenic viewpoints like Yamdrok Lake and Gyatso La Pass.
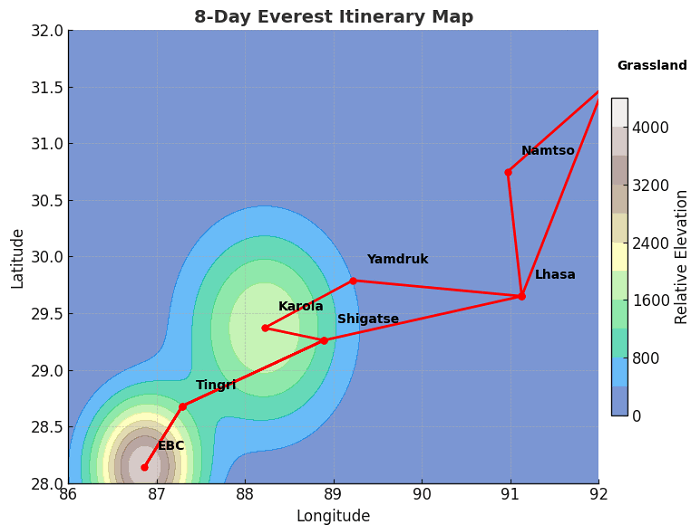
Lhasa to Everest Base Camp Itinerary Map
5. Nepal Everest Trekking Map
Nepal stakes its claim as the trekking capital of the world, and the Lukla–EBC trail stands as its crown jewel:
- Stage 1: Lukla (2,860 m) ➔ Phakding (2,610 m)
- Stage 2: Phakding ➔ Namche Bazaar (3,440 m)
- Stage 3: Acclimatization day at Namche Bazaar
- Stage 4: Namche Bazaar ➔ Tengboche (3,860 m)
- Stage 5: Tengboche ➔ Dingboche (4,360 m)
- Stage 6: Dingboche ➔ Lobuche (4,940 m)
- Stage 7: Lobuche ➔ Everest Base Camp (5,364 m) ➔ Gorak Shep (5,164 m)
Highlights Along the Way:
- Ancient temples in Kathmandu Valley (Durbar Squares, Pashupatinath, Boudhanath) before departure
- Rhododendron forests and Sagarmatha’s wildlife
- Sherpa villages such as Khumjung, where Everest legends come alive
- Close‑up vistas of Ama Dablam, Lhotse and Nuptse
When planning, refer to a Nepal trekking map that shows lodge locations, rest days, emergency shelters and altitude profiles for each segment.
6. Mt. Everest Climbing Route Map (North Ridge)
The north ridge route from Tibet is recognized as more technically demanding, but also less crowded than the south face:
- Base Camp: 5,200 m
- Advanced Base Camp: 6,492 m
- North Col (Camp 1): 7,000 m
- Camp 2: 7,500 m
- Camp 3: 8,300 m (Yellow Band)
- First Step: 8,500 m
- Second Step: 8,577 m (fixed ladders over a near‑vertical rock face)
- Third Step: 8,690 m
- Summit Pyramid: 8,800 m
- Summit: 8,844.43 m
A detailed climbing‑route map will depict fixed rope sections, ladder crossings, crevasse fields and ideal camp locations, ensuring climbers can plot turnaround times and oxygen‐drop sites.
7. Costs, Summits and Safety Statistics
Average Cost to Climb Everest: USD 30,000–50,000
(Includes travel, permit fees, insurance, equipment rental, logistics, Sherpa support)
Summit Totals (through 2015):
- Tibet Side: 2,580 successful ascents; 106 fatalities
- Nepal Side: 4,421 successful ascents; 176 fatalities
Main Climbing Risks:
- Altitude sickness (HACE, HAPE)
- Avalanches and icefall collapses
- Extreme cold, exhaustion and frostbite
- Falls on steep slopes and crevasse plunges
Everest maps intended for climbers should annotate known hazard zones, recommended high‑altitude camp sites, rescue shelters and safe descent routes.
8. Practical Preparation and Permits
Tibetan Side Permits:
- Tibet Travel Permit
- Alien’s Permit for border zones
- Mountaineering Expedition Permit (for climbers)
Nepal Side Permits:
- Sagarmatha National Park Entry Permit
- Khumbu Pasang Lhamu Rural Municipality Permit
- TIMS Card (Trekkers’ Information Management System)
Altitude Acclimatization Tips:
- Gradual ascent (no more than 500 m overnight gain above 3,000 m)
- Hydration, rest days and possible Diamox medication
Gear Essentials:
- Layered cold‑weather clothing and mountaineering boots
- Crampons, ice axe and harness for technical climbs
- Sleeping bag rated to –20 °C or lower for nights at high camps
An Everest expedition map should feature permit pickup points (Kathmandu, Lhasa), acclimatization hotels in Namche or Tingri, and recommended gear shops in major cities.
Mapping Your Everest Adventure
Whether you yearn to stand atop the world in triumph or simply to trace the outlines of Everest on a high‑definition map, a well‑designed Mt. Everest map is your essential companion. From the accessible North Base Camp roads of Tibet to Nepal’s storied Khumbu trails, each route offers unique vistas, cultural insights and logistical considerations. By studying elevation profiles, camping sites, hazards and permit requirements, you can craft an itinerary that balances ambition with safety.
Plan Your Everest Expedition with China Dragon Travel
At China Dragon Travel, we specialize in tailor‑made Everest and Tibet tours. Our comprehensive services include permit arrangement, acclimatization itineraries, experienced Sherpa guides, 4×4 transfers, high‑quality camping gear and emergency support. Contact us today to chart your path to Mt. Everest.












